by Katrina S. Dudley, CFA, Investment Strategist, Portfolio Manager, Franklin Mutual Series
Mandana Hormozi, Portfolio Manager, Research Analyst, Franklin Mutual Series
Tim Rankin, CFA, ESG Ambassador for Franklin Mutual Series, Portfolio Manager & Research Analyst, &
Todd Ostrow, Portfolio Manager, Research Analyst, Franklin Mutual Series
After years lagging the tech-heavy US market, Franklin Mutual Series sees international value stocks coming back into the spotlight over the coming years as the traditional economy comes into sharper focus.
Global investing is facing a sea change. After a decade of low interest rates, slight inflation, and plenty of central bank support pushing US growth stocks to dizzying heights, international value stocks now look to us to be in the early days of a revival as these trends reverse. The international companies that finance, build and power the traditional global economy are overtaking the US firms that had dominated market performance. Companies in the more conventional value markets like Europe and Japan are back in style. Not only are these leading firms attractively valued, in our view, but they also offer economic exposure to both US and emerging markets and can benefit from recent government spending initiatives.
International companies are leading firms
For many US-based investors, international stocks can often be an afterthought. This home-country bias means that US investors ignore some of the leading companies in their fields that just happen to be listed in Europe or Asia in favor of their US equivalents.
Many of these non-US companies are at the forefront of industries such as luxury goods, advanced auto components, pharmaceuticals, consumer products, banking, machinery and industrial equipment, and payments. Technological advances are reverberating through many of these industries and the benefits of digitization, machine learning and artificial intelligence are increasingly driving productivity improvements beyond just the technology sector.
Additionally, international markets tend to be less efficient than the US stock market, meaning these best-in-class companies may have fewer analysts covering them, and information on them may be less readily available. Fewer analysts doing high-quality research can lead to more inefficient pricing, creating a valuation gap between US and non-US companies. Investors willing to do greater fundamental analysis can identify attractive investments that others might overlook. And with less investor and analyst focus, international markets can be a catalyst-rich hunting ground for finding undervalued stocks with the potential to unlock value for shareholders over time.
International markets are cheap, cheap, cheap
As a result of this inefficiency, US investors’ bias for homegrown companies, and the decade-long rush into the growthy technology stocks that dominate the US equity market, the valuation gap between the US market and international stocks has widened significantly.1 (See Exhibit 1.) We think this disparity suggests greater room for non-US companies’ valuations to improve over time, with additional tailwinds from the more favorable interest-rate regime and modest inflationary environment that tend to benefit value-type companies. Historically, we have seen value stocks outperform growth stocks as interest rates climb, and they tend to be better positioned than growth companies to pass higher prices along to customers.
Exhibit 1: Price to Earnings: MSCI USA vs. MSCI EAFE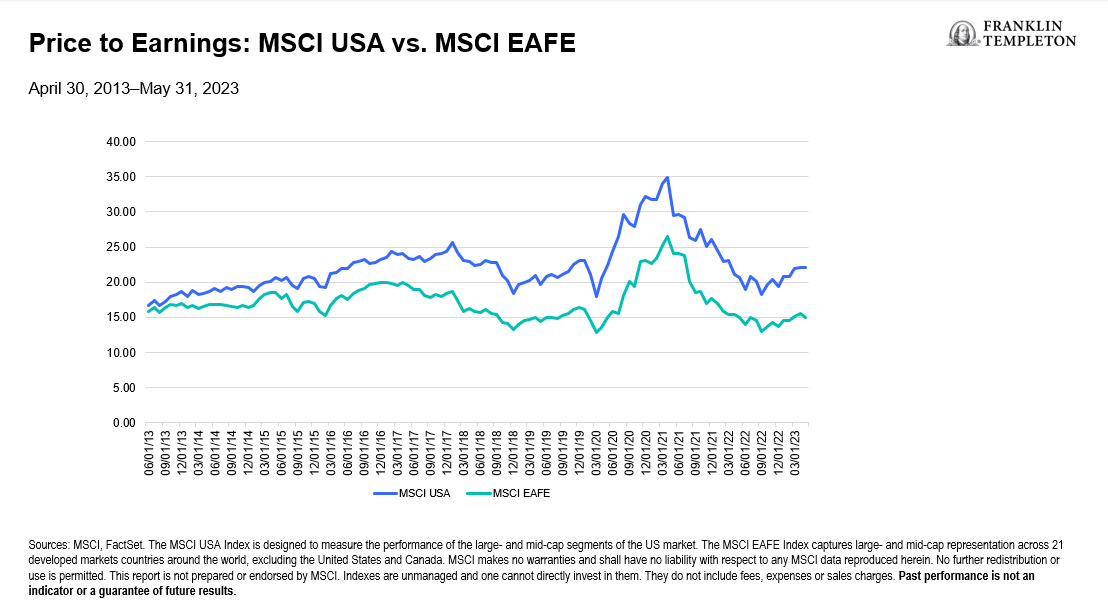
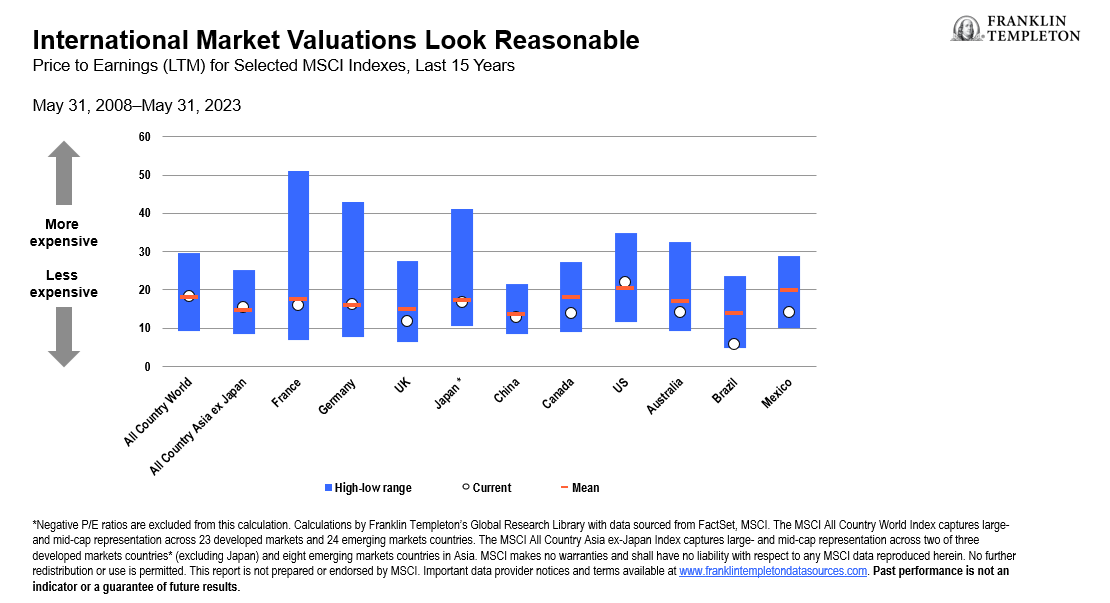
Furthermore, valuations for individual Asian and European markets are well below their mean and at the bottom end of the range seen over the past 15 years.2 (See Exhibit 2.) The US equity market, meanwhile, sits above both its mean and the valuations of other major developed markets, making it more expensive by comparison, with possibly less potential upside than Asian and European markets.
Exhibit 2: International Market Valuations Look Reasonable
International value stocks are cheaper still, with the MSCI EAFE Value Index sitting near 10-year low valuation multiples, with a price/earnings (P/E) ratio of 10.4 times, compared to the 25.9 times for the MSCI EAFE Growth Index, according to data from FactSet.3 (See Exhibit 3). In our view, international value stocks offer further upside potential for investors willing to do in-depth fundamental research to find attractively valued companies with compelling ways to improve their valuations. Additionally, they can benefit from the higher inflation and interest rates seen in many non-US markets over the past year.
Exhibit 3: Price to Earnings: MSCI EAFE Growth vs. MSCI EAFE Value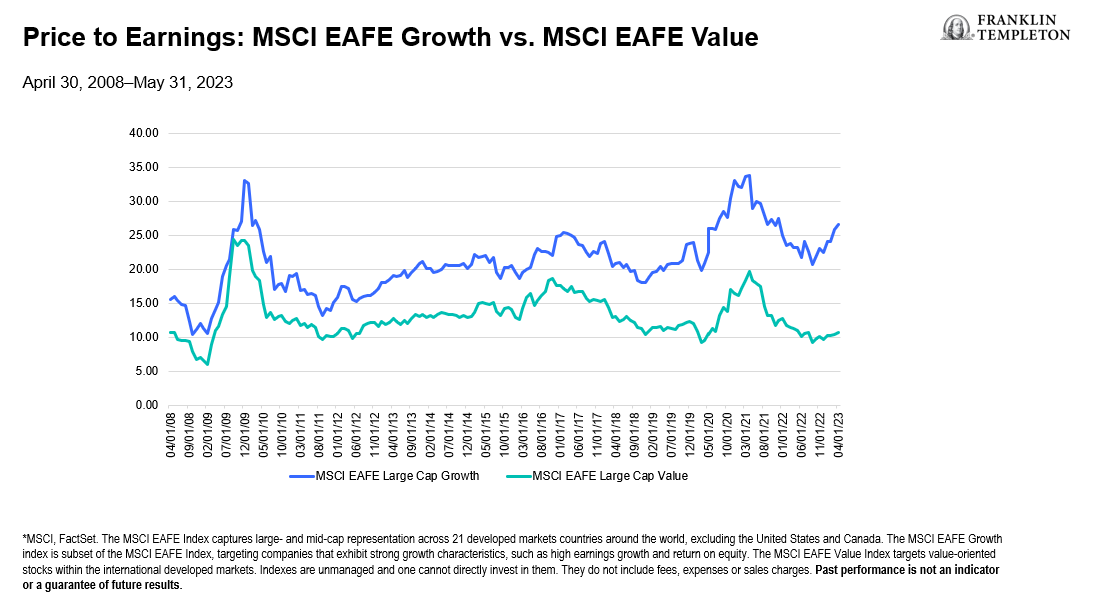
Non-US companies offer global exposure
International stocks are not only relatively cheap with what we believe are better prospects to improve their valuations, but many companies in Europe and Asia are global businesses that offer both an anchor to the stability of the US economy and exposure to many attractive fast-growing emerging markets. The proportion of MSCI EAFE Index earnings that is generated outside of home countries is significant. About a fifth of all MSCI EAFE Index revenue is generated in the United States, while another 20% comes from emerging and frontier markets, according to data from FactSet.
Emerging markets are expected to contribute to 60% of global gross domestic product growth, according to data from the International Monetary Fund’s World Economic Outlook as of April 2023, making them important drivers of the world economy. For investors who like the growth emerging markets can bring, investing internationally can provide investors with greater exposure to those markets without the potential risks of investing in companies listed in sometimes more opaque and less-stable regions.
Furthermore, the international value index can offer exposure to recent strong performing markets such as Japan. Although Japan makes up almost 30% of MSCI EAFE Value Index, it accounts for more than 14% of index revenues, according to data from FactSet as of June 2023. As the economy continues to reopen after the pandemic and as inflation exerts itself a bit more forcefully, Japanese stocks could benefit as export-led growth gives way to more domestic consumption.
Meanwhile, relying on the S&P 500 Index for global exposure may not give investors significant international exposure. The United States accounts for 60% of sales for S&P 500 Index constituents, with China the next largest market at about 7.5%, according to FactSet data as of June 2023. An investment in non-US markets may be a suitable alternative for investors looking for international exposure without becoming unmoored from US economic stability.
A boost from government spending
Beyond exposure to faster-growing regions, international companies stand to benefit from the massive government spending enacted over the past few years. The United States and European Union (EU) are looking to make their supply lines more secure, bring manufacturing closer to home and green their economies. International industrials, energy and materials companies are likely to be major beneficiaries of these efforts to invest in the more traditional economy. Companies are also looking to move manufacturing facilities closer to their customers and create more resilient supply chains following the lessons of the pandemic and heightened geopolitical tensions.
In energy, for instance, both the impact of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and recent US climate-change mitigation and energy security legislation are likely to result in greater investment opportunities for those European companies focused on green energy and renewable power initiatives. The EU’s Green Deal, meanwhile, looks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 through investments in cleaner energy, making buildings more energy efficient and establishing more public transportation. Even Japan, which has been reluctant to commit to ending its dependence on coal and other fossil fuels, has begun to talk about an eventual phase out of these fuels. Overall, clean energy investments are ramping up and could reach about US$1.7 trillion this year, according to the International Energy Agency. (See Exhibit 4.)
Exhibit 4: Investment in Clean Energy to Hit US$1.7 Trillion in 2023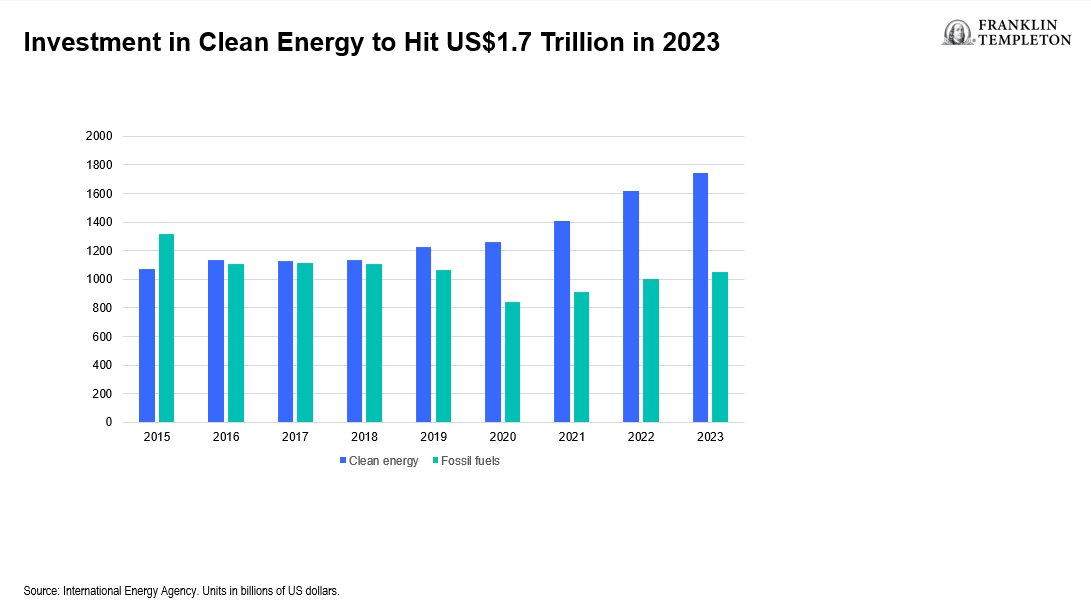
Meanwhile, Japan is slowly improving its lackluster governance policies. Better corporate governance could lead to a greater focus on shareholder returns, meaning more emphasis on improving business returns as well as higher dividends or potentially larger share repurchases over time. One reason for the Japanese market’s paltry relative valuation is that, according to data from FactSet as of June 2023, returns on equity are among the lowest in the developed world.
From attractive fundamentals, cheap valuations, global reach, and the benefits of newly announced government spending programs, we think European and Asian stock markets are rich hunting grounds for attractive value companies poised to benefit from a changing investment regime. To find these international opportunities, we think a deep understanding of company valuations and the ways in which these firms can unlock value for shareholders is crucial.