by Sound Choices, AGF Management Ltd.
Insights and Market Perspectives
Author: Sound Choices
March 26, 2020
Bear Markets: What You Need to Know
There’s been a lot of talk recently about the stock markets moving into bear territory. What does that mean and what do you need to know?
What is a bear market?
A bear market is triggered by a market decline of 20%. Each stock market will enter bear market territory at slightly different times depending on when they reach that 20% drop.
What caused the current bear market?
This stock market volatility was influenced by the uncertainty of the COVID-19 pandemic. Looking back, previous epidemics haven’t caused significant market turmoil. That said, the severity of this virus and length of the epidemic could continue to impact what happens in the market.
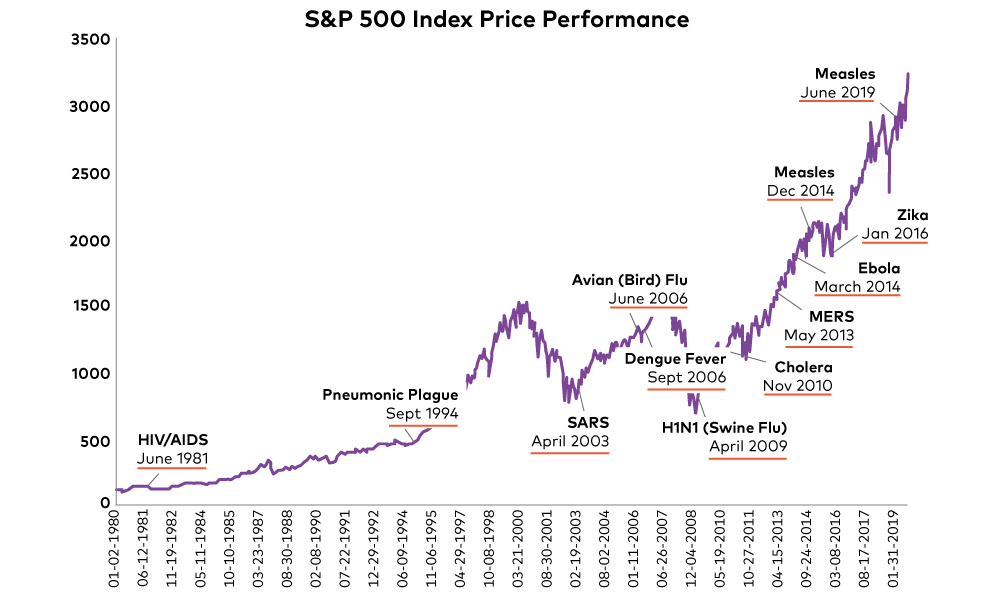
Source: Bloomberg. *12-month data is not available for June 2019 measles.
Bear market ≠ economy
A market decline doesn’t necessarily mean that the economy is in trouble. That said, a bear market can occur hand in hand with an economic recession – which is defined by the economy experiencing two or more quarters of negative growth (or decline). As with the stock markets, individual economies can go into recession at different times.
With the current environment – schools being closed, employees working from home or quarantined, travel restricted – much of the economy is at a stand-still and the data will undoubtedly reflect that.
Previous bear markets
No one can predict exactly how far the stock market will drop and when it will bottom out. Nor can they say precisely how long a bear market will last.
The table below shows the biggest market corrections over the last century. It’s important to remember that the recent end to the 11-year bull market wasn’t triggered by the stocks being overvalued as with with the dotcom crash. Nor was it an indicator of systemic issues like the Global Financial Crisis.
| Bear Market | S&P500 loss |
|---|---|
| Wall Street Crash Sept. 1929 – June 1932 The stock market crash of Oct. 29, 1929 marked the start of the Great Depression. |
86.1% |
| Post WW2 May 1946 – June 1949 Less than a year after the end the war, stock prices peaked and began a long slide. |
29.6% |
| Oil shock / recession Jan. 1973 – Oct. 1974 Israel's Yom Kippur War and the subsequent Arab oil embargo sent energy prices soaring, sparking a lengthy recession. |
48.0% |
| Stagflation (high inflation + slow growth) Nov. 1980 – Aug. 1982 After nearly a decade of sustained inflation, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to nearly 20%, pushing the economy into recession. |
27.8% |
| Black Monday Aug. 1987 – Dec. 1987 After a prolonged bull run, computerized "program trading" strategies swamped the market and contributed to the Black Monday crash of Oct. 19. |
33.5% |
| Dotcom crash March 2000 – Oct. 2002 The bursting of the dot-com bubble followed a period of soaring stock prices and exuberant speculation on new Internet companies. |
49.1% |
| Great Financial Crisis Oct. 2007 – March 2009 A long-feared bursting of the housing bubble became a reality beginning in 2007, and the rising mortgage delinquency rate quickly spilled over into the credit market. |
56.4% |
Source: Global Financial Data, msnbc.com research. http://www.nbcnews.com/id/37740147/ns/business-stocks_and_economy/t/historic-bear-markets/#.XnTLLqhKj4Y
How long does a bear market last?
The average bear market lasts less than a year.
The chart below shows the bull and bear markets in the Canadian stock market over the past 60-plus years. The bull markets (purple line) on average lasted longer (42.9 months vs. 8.6 months) and their average gain (105.8%) was higher than the average drop during the bear markets (24.7%).
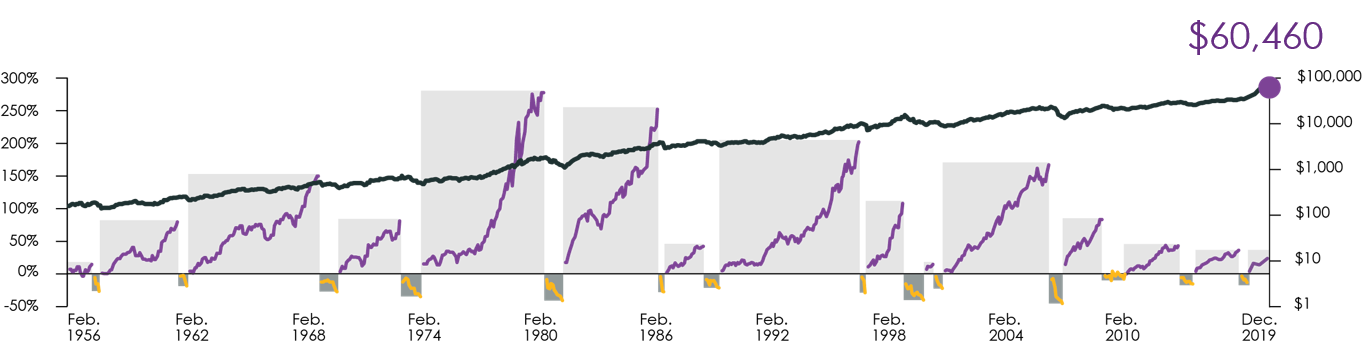
Source: Bloomberg and Morningstar Direct, S&P/TSX Composite Total Return Index, February 1, 1956 – December 31, 2019. The information provided is for illustrative purposes only and is not meant to provide investment advice. You cannot invest directly in an index.
How can you protect yourself from the bear?
As in real life, you probably shouldn’t run from a bear (market).
Reach out to your financial advisor who can help ensure your portfolio is diversified appropriately for your risk level, investment goals and time horizon.
And if you have questions about market volatility, visit AGF.com/volatility. There you’ll find articles and videos that discuss the current markets as well as providing context and tips for managing volatility on an ongoing basis.
About AGF Management Limited
Founded in 1957, AGF Management Limited (AGF) is an independent and globally diverse asset management firm. AGF brings a disciplined approach to delivering excellence in investment management through its fundamental, quantitative, alternative and high-net-worth businesses focused on providing an exceptional client experience. AGF’s suite of investment solutions extends globally to a wide range of clients, from financial advisors and individual investors to institutional investors including pension plans, corporate plans, sovereign wealth funds and endowments and foundations.
For further information, please visit AGF.com.
© 2020 AGF Management Limited. All rights reserved.
This post was first published at the AGF Perspectives Blog.