by Gene Podkaminer, CFA, Franklin Templeton Investments
During normal times, rebalancing a portfolio is a relatively mundane exercise, an activity that can be performed succinctly and often mechanically. But when markets gyrate, as they have recently, an investor’s approach to rebalancing becomes much more complex. And unlike many other aspects of investing, rebalancing is somewhat of a dark art with few universally accepted rules. Ultimately, rebalancing is the feedback loop between your actual portfolio and the carefully crafted asset-allocation ranges you devised in calmer times.
Over the past several months, we have observed price declines in many assets considered riskier (such as the many flavours of equity), coupled with mixed performance or even appreciation in assets considered less risky, such as bonds. Of course, the prices of investments which aren’t marked-to-market, such as appraisal-based private equity and real estate, may lag their public-market peers by several quarters, but economically investors should expect those assets to move alongside their public-market cousins.
What is an investor to do when their thoughtfully constructed asset allocation comes in contact with the financial aftermath of COVID-19? Allow it to drift? Micro-manage the investments to precisely match target ranges? Perhaps a bit of both?
We’ve observed asset allocators adopt a wide range of responses to these questions, with some allowing portfolios to drift hands-off while others aggressively true up to ranges. Many institutional and professional investors formally document their portfolio weights, while individuals may take a less formal approach. But that doesn’t change the calibration of a mix of assets to a certain risk tolerance, whether expressed explicitly as the Greek letter λ (lambda) in an optimiser, or implicitly as a static proportion of stocks vs. bonds for those less versed in Greek. So, allowing a portfolio’s allocation to unintentionally drift implies that the risk level has also drifted away from the target.
A Reminder: Why Should You Rebalance?
Let’s take a step back to recall the central idea underlying rebalancing. Rebalancing enables an investor to maintain a consistent mix between more risky and less risky assets through changing market conditions. A disciplined rebalancing process should mathematically translate to a more stable risk journey over time, instead of one which mirrors the ups and downs of equity markets (We’re picking on equities because they tend to be the riskiest investment in most portfolios).
Ignoring rebalancing entirely means that the important diversification choices you likely have built into your portfolio are effectively undone. Rebalancing is, by design, contrarian. And we’ve learned from behavioural finance that such counter-cyclical behaviour will likely lead to some degree of discomfort in the moment.
Exhibit 1 below graphs two illustrative approaches: Portfolio A is rebalanced monthly, and Portfolio B is never rebalanced. The top two lines graph the cumulative wealth of both portfolios, with each starting at US$100 10 years ago (on 1 March 2010). We look at annualised standard deviation as a proxy for risk and observe similar results: Portfolio A has experienced less risk over the past 10 years vs. Portfolio B. Combined, both of these attributes lead to Portfolio A retaining more of its wealth because of the smoother ride resulting from lower standard deviation, it experienced less of the “volatility penalty”.
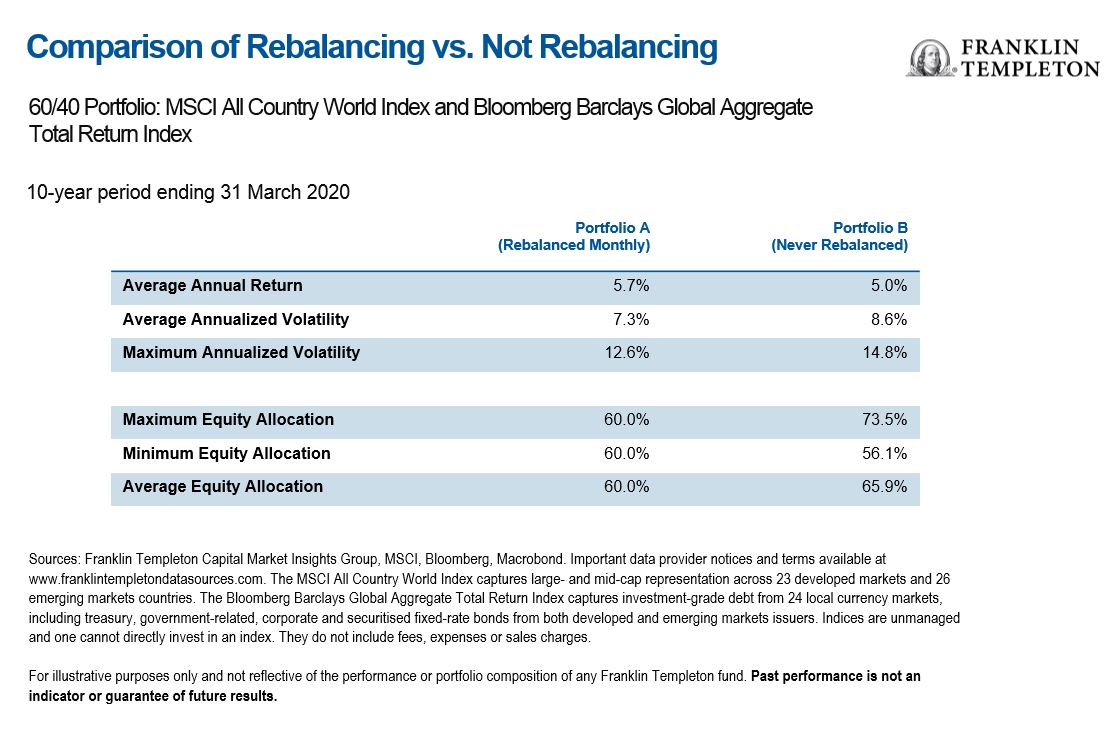
The table in Exhibit 2 helps us quantify the graph further. In Portfolio B, the equity allocation swings around from 56.1% to 73.5%, which contrasts with the steady 60% allocation for Portfolio A. The volatility rises from 7.3% to 8.6% without rebalancing, and that impacts the overall return, which falls from 5.7% to 5.0%. Note that we ran similar analyses over the past 20 and 30 years, also using quarterly as well as monthly rebalancing, and arrive at similar conclusions.
Exhibit 1: Rebalancing Vs. No Rebalancing 60/40 Portfolio: Monthly (right click to enlarge)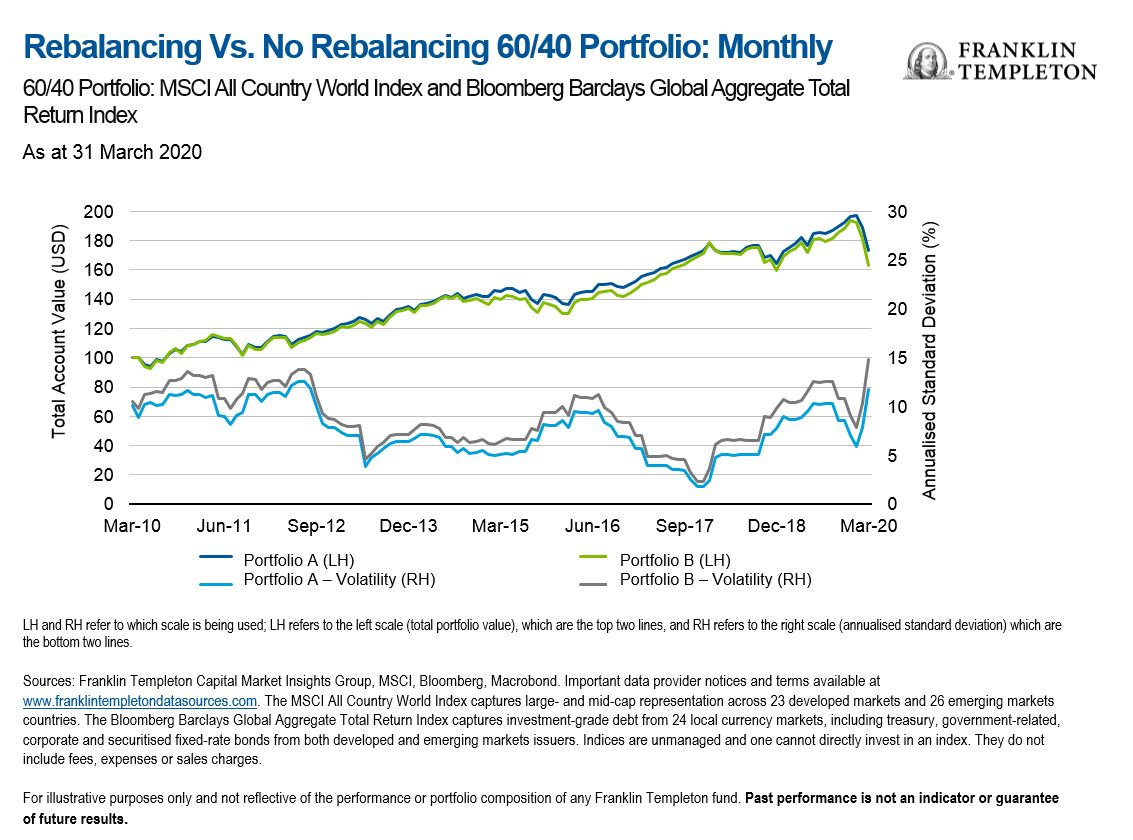
Exhibit 2: Comparison of Rebalancing Vs. Not Rebalancing (right click to enlarge)
But, of course, it’s never quite that easy. Rebalancing involves transacting in the market, which means buying and selling—and all of the costs and frictions associated with those activities, including commissions and taxes. Which leads us to ask: what is a balanced approach to rebalancing?
The Range of Rebalancing Options—and Considerations
We ask several questions of rebalancing: when should we rebalance, should we rebalance to an outer range or all the way back to a target weight, and when should we let rebalancing slide? To answer these questions, and more, let’s discuss three common approaches:
- Calendar-based rebalancing: the simplest method, this could be quarterly, but some use monthly or annual cycles. (We use this approach in Exhibits 1 and 2.)
- Range-based rebalancing: when a given investment is outside some prespecified range, action is recommended. Many institutional investors with formal investment policy statements use this approach.
- Risk-based rebalancing: shifting the mix of assets when striving to keep the overall portfolio risk level close to a prespecified target. If equities are expected to contribute more risk to the overall portfolio going forward, then their weight would be proportionally reduced to maintain the desired overall risk level.
We mentioned transaction costs, taxes, and other frictions earlier, but there are also several other factors to consider before rebalancing, including these two:
- How willing are you to let momentum ride, that is, for recent strong performers to continue instead of trimming them back?
- Are you constrained from rebalancing by holding illiquid investments, which determine the denominator of your portfolio?
For instance, if your investments are taxable, then a potential rebalancing move could be weighed against the explicit tax cost, in addition to any execution cost. If you believe in momentum, then you may justify wider allowable ranges. However, if you think mean reversion (where assets return to their long-run average valuation over time) is prevalent, that may encourage a slower rebalancing cadence, with more patience involved as you wait for prices to adjust closer to historical averages. And illiquid assets often simply cannot be rebalanced because of the very high trading costs (and price haircuts)—not to mention delays—that may be involved. Your approach to rebalancing says a lot about how you view the future, whether you believe in momentum or reversion back to the mean.
If you’re utilising a range-based approach, how far back into the range do you go? Let’s assume that you have a 60% global equity, 40% global fixed income portfolio with a ±5% range around each. If your portfolio currently reads 50% equity, 50% fixed income, do you rebalance back to targets (60%/40%) or to the edge of the range (55%/45%)? We’ve observed that many do the latter (to the edge) because the cost and disruption of transacting can be high.
Also, investors may have the opportunity to “virtually” rebalance using new funds to top up underweight asset classes, or conversely to fund necessary withdrawals from overweight asset classes. Unless the portfolio composition is substantially distorted, phasing back to target weights may be an equally effective, if lighter-touch approach.
The concept of using new funds or contributions to, or withdrawals from, the portfolio to align weights can be used in situations where regular cash flows occur (regardless of direction), such as pension funds, individual retirement accounts and college savings programmes. Topping-up underweight asset classes or pulling funds from overweight asset classes provides for dollar-cost-averaging vs. a one-time “big-bang” rebalance, thus maintaining a contrarian mindset, which can be helpful in times of market turmoil.
What Do Others Do?
Many may be wondering how sophisticated institutional investors approach rebalancing challenges. Some use so-called “overlay” programmes where a small dedicated cash sleeve is invested in equity and fixed income derivatives, creating levered synthetic positions which can then be quickly and seamlessly changed to ensure the overall portfolio exposures stay in balance. But an overlay program only has so much reach; at some point rebalancing among the portfolio components is necessary, and the overlay proportions reset.
Some institutions carefully manage new fund flows to stay within acceptable ranges, though at some point selling relatively better-performing assets is still required. For those institutions which use a factor-based asset allocation approach, the risk-based rebalancing approach is a good fit because they approach investing from a risk-first posture.
Contemplating a rebalancing discipline is as much about reducing risk as eking out some marginal return. Our focus has been on examining rebalancing through a risk management lens as investors can attempt to control risks, while forward-looking returns are unknown. For many investors, the prospect of a smoother ride is a compelling reason to consider adjusting a drifting portfolio back into spec. These are not simple questions, and each investor has a unique approach to rebalancing, whether quarterly to the edge of the range or a one-time shift back to target.
Rebalancing shouldn’t be thought of as a stand-alone discipline; instead, it is just one part of a comprehensive approach to asset allocation and risk management.
Important Legal Information
This material is intended to be of general interest only and should not be construed as individual investment advice or a recommendation or solicitation to buy, sell or hold any security or to adopt any investment strategy. It does not constitute legal or tax advice.
The information provided is not a recommendation or individual investment advice for any particular security, strategy, or investment product and is not an indication of the trading intent of any Franklin Templeton managed portfolio. This is not a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any industry, security or investment and should not be viewed as an investment recommendation. This is intended to provide insight into the portfolio selection and research process. Factual statements are taken from sources considered reliable but have not been independently verified for completeness or accuracy. These opinions may not be relied upon as investment advice or as an offer for any particular security. Past performance is not an indicator or a guarantee of future results.
The views expressed are those of the investment manager and the comments, opinions and analyses are rendered as of publication date and may change without notice. The information provided in this material is not intended as a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any country, region or market.
Data from third party sources may have been used in the preparation of this material and Franklin Templeton (“FT”) has not independently verified, validated or audited such data. FT accepts no liability whatsoever for any loss arising from use of this information and reliance upon the comments, opinions and analyses in the material is at the sole discretion of the user.
Products, services and information may not be available in all jurisdictions and are offered outside the U.S. by other FT affiliates and/or their distributors as local laws and regulation permits. Please consult your own professional adviser or Franklin Templeton institutional contact for further information on availability of products and services in your jurisdiction.
Issued in the U.S. by Franklin Templeton Distributors, Inc., One Franklin Parkway, San Mateo, California 94403-1906, (800) DIAL BEN/342-5236, franklintempleton.com—Franklin Templeton Distributors, Inc. is the principal distributor of Franklin Templeton Investments’ U.S. registered products, which are not FDIC insured; may lose value; and are not bank guaranteed and are available only in jurisdictions where an offer or solicitation of such products is permitted under applicable laws and regulation.
What Are the Risks?
All investments involve risks, including possible loss of principal. The value of investments can go down as well as up, and investors may not get back the full amount invested. Diversification does not guarantee profits or eliminate the risk of investment losses. Stock prices fluctuate, sometimes rapidly and dramatically, due to factors affecting individual companies, particular industries or sectors, or general market conditions. Bond prices generally move in the opposite direction of interest rates. Thus, as the prices of bonds in an investment portfolio adjust to a rise in interest rates, the value of the portfolio may decline. Special risks are associated with foreign investing, including currency fluctuations, economic instability and political developments. Investments in emerging markets, of which frontier markets are a subset, involve heightened risks related to the same factors, in addition to those associated with these markets’ smaller size, lesser liquidity and lack of established legal, political, business and social frameworks to support securities markets. Because these frameworks are typically even less developed in frontier markets, as well as various factors including the increased potential for extreme price volatility, illiquidity, trade barriers and exchange controls, the risks associated with emerging markets are magnified in frontier markets.
This post was first published at the official blog of Franklin Templeton Investments.