by Don Vialoux, EquityClock.com
Technical Notes released yesterday at
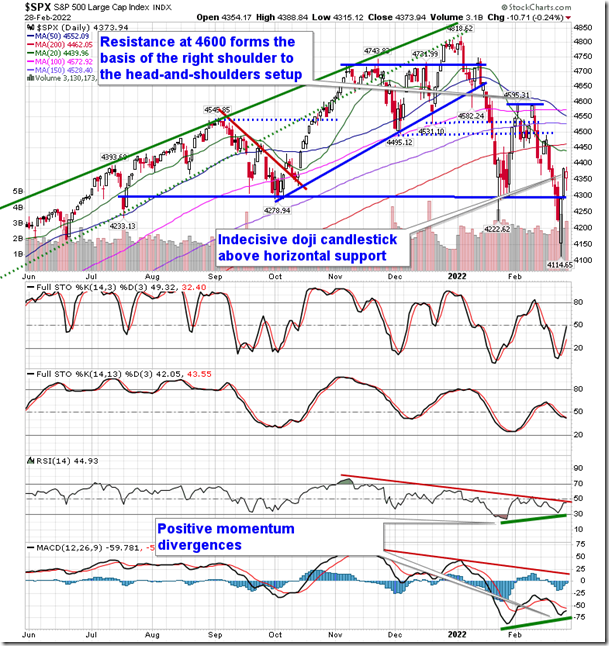
S&P 500 Index charts a rather indecisive doji candlestick just above support at 4280. equityclock.com/2022/02/28/… $SPX $SPY $ES_F
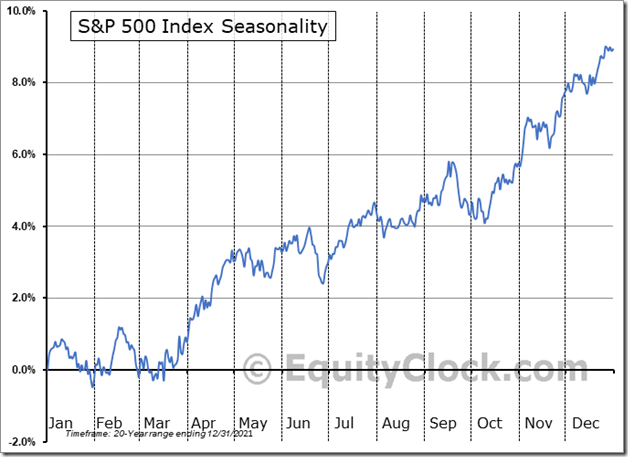
The large-cap benchmark has gained an average of 1.0% in the month of March with 60% of periods closing higher over the past two decades. $STUDY $SPX $SPY $ES_F
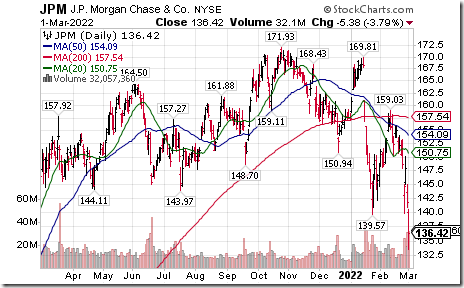
JP Morgan $JPM a Dow Jones Industrial Average stock moved below $139.57 extending an intermediate downtrend.
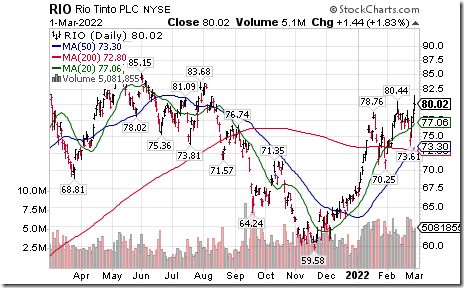
Rio Tinto $RIO one of the largest base metal producers in the world moved above $80.44 extending an intermediate uptrend.
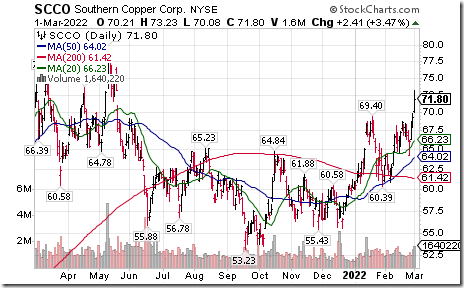
Southern Copper $SCCO one of the largest copper producers in the world moved above $69.40 extending an intermediate uptrend. Seasonal influences are favourable to mid-April. If a subscriber to EquityClock, see seasonality chart at https://charts.equityclock.com/southern-copper-corp-nysescco-seasonal-chart
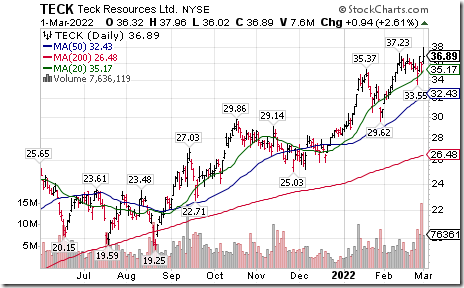
Another base metals equity breakout! Teck Resources $TECK moved above US$37.23 and $TECK.B.CA moved above Cdn$47.07 extending an intermediate uptrend. Seasonal influences are favourable until at least early May. If a subscriber to EquityClock, see seasonality chart at
https://charts.equityclock.com/teck-resources-ltd-nyseteck-seasonal-chart
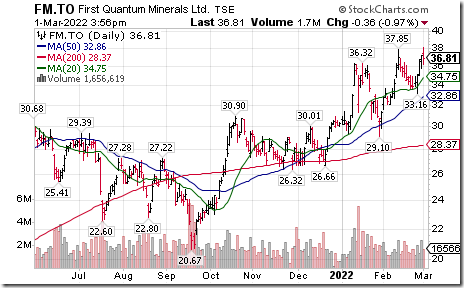
Another Canadian base metal producer breakout! First Quantum Minerals $FM.CA a TSX 60 stock moved above $37.85 extending an intermediate uptrend. Seasonal influences are favourable until at least early May. If a subscriber to EquityClock, see seasonality chart at
https://charts.equityclock.com/first-quantum-minerals-limited-tsefm-seasonal-chart
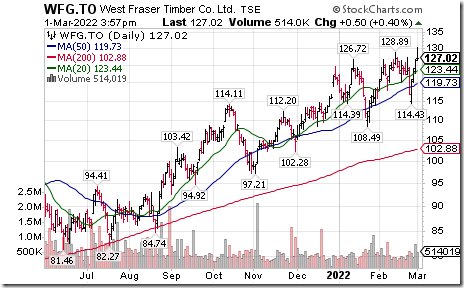
Forest product stocks are moving higher once again. West Fraser Timber $WFG.CA moved above Cdn$128.89 to an all-time high extending an intermediate uptrend.
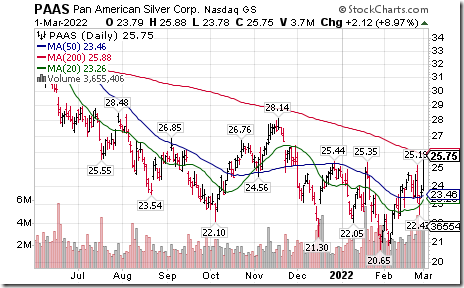
Silver equities and related ETF $SIL are responding to the spike in silver futures prices. Panamerican Silver $PAAS moved above intermediate resistance at $25.44 and $25.35.
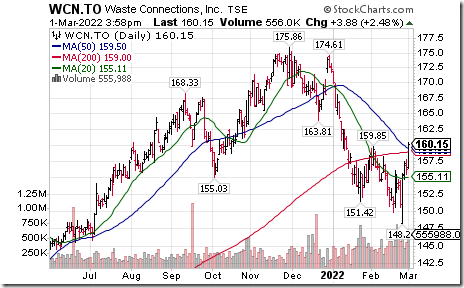
Waste Connections $WCN.CA a TSX 60 stock moved above intermediate resistance at $159.85
Trader’s Corner
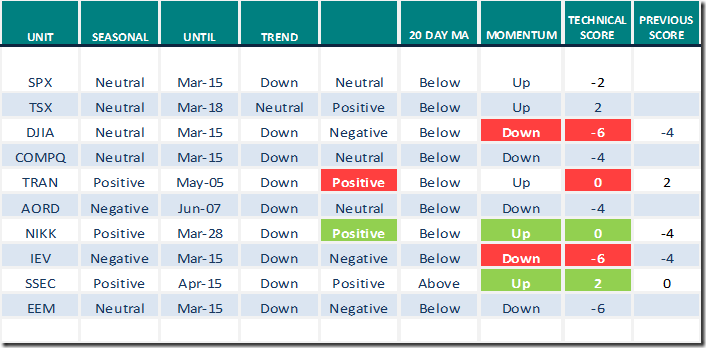
Equity Indices and Related ETFs
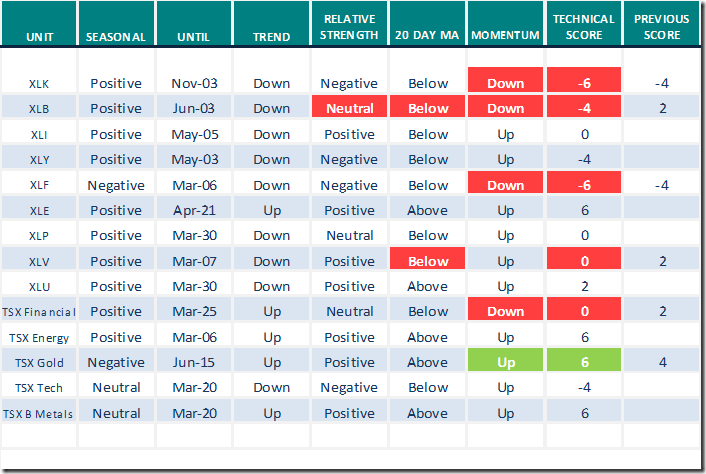
Daily Seasonal/Technical Equity Trends for March 1st 2022
Green: Increase from previous day
Red: Decrease from previous day
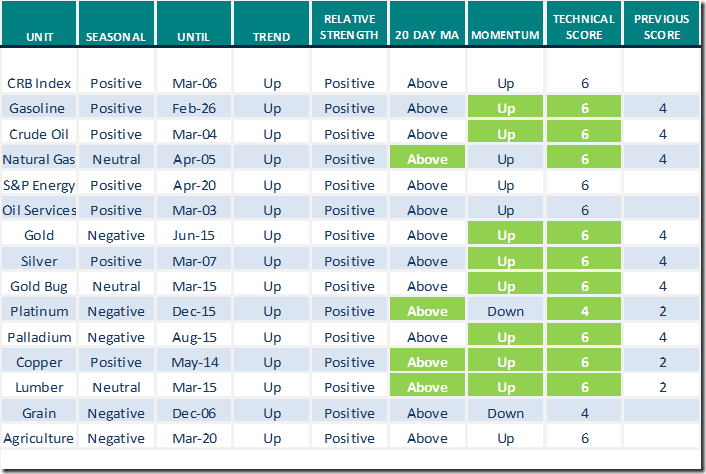
Commodities
Daily Seasonal/Technical Commodities Trends for March 1st 2022
Green: Increase from previous day
Red: Decrease from previous day
Sectors
Daily Seasonal/Technical Sector Trends for March 1st 2021
Green: Increase from previous day
Red: Decrease from previous day
All seasonality ratings are based on performance relative to the S&P 500 Index (except TSX)
What’s up is space
A major volcanic eruption recently occurred in the South Pacific that could have a significant impact on world climate during the next 2-3 years. The plume of ash and aerosol in the atmosphere from the eruption was 1.5 times the height reached by the Mount Pinatubo eruption in 1991.
World temperatures dropped significantly for the next 2-3 years following the Mount Pinatubo eruption. Following is an article showing the aftermath of the Mount Pinatubo eruption:
‘On June 15, the eruption of Mount Pinatubo began at 1:42 p.m. local time. The eruption lasted for nine hours and caused numerous large earthquakes due to the collapse of the summit of Mount Pinatubo and the creation of a caldera. The caldera reduced the peak from 1745 meters (5725 feet) to 1485 meters (4872 feet) high is 2.5 kilometers (1.5 miles) in diameter.
Unfortunately, at the time of the eruption Tropical Storm Yunya was passing 75 km (47 miles) to the northeast of Mount Pinatubo, causing a large amount of rainfall in the region. The ash that was ejected from the volcano mixed with the water vapor in the air to cause a rainfall of tephra that fell across almost the entire island of Luzon. The greatest thickness of ash deposited 33 centimeters (13 inches) approximately 10.5 km (6.5 mi) southwest of the volcano. There was 10 cm of ash covering an area of 2000 square kilometers (772 square miles). Most of the 200 to 800 people (accounts vary) who died during the eruption died due to the weight of the ash collapsing roofs and killing two occupants. Had Tropical Storm Yunya not been nearby, the death toll from the volcano would have been much lower.
In addition to the ash, Mount Pinatubo ejected between 15 and 30 million tons of sulfur dioxide gas. Sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere mixes with water and oxygen in the atmosphere to become sulfuric acid, which in turn triggers ozone depletion. Over 90% of the material released from the volcano was ejected during the nine-hour eruption of June 15.
The eruption plume of Mount Pinatubo’s various gasses and ash reached high into the atmosphere within two hours of the eruption, attaining an altitude of 34 km (21 miles) high and over 400 km (250 miles) wide. This eruption was the largest disturbance of the stratosphere since the eruption of Krakatau in 1883 (but ten times larger than Mount St. Helens in 1980). The aerosol cloud spread around the earth in two weeks and covered the planet within a year. During 1992 and 1993, the Ozone hole over Antarctica reached an unprecedented size.
The cloud over the earth reduced global temperatures. In 1992 and 1993, the average temperature in the Northern Hemisphere was reduced 0.5 to 0.6°C and the entire planet was cooled 0.4 to 0.5°C. The maximum reduction in global temperature occurred in August 1992 with a reduction of 0.73°C. The eruption is believed to have influenced such events as 1993 floods along the Mississippi River and the drought in the Sahel region of Africa. The United States experienced its third coldest and third wettest summer in 77 years during 1992.
Overall, the cooling effects of the Mount Pinatubo eruption were greater than those of the El Niño that was taking place at the time or of the greenhouse gas warming of the planet. Remarkable sunrises and sunsets were visible around the globe in the years following the Mount Pinatubo eruption.’
Following is an article published by Mark Leibovit and www.spaceweather.com that offers information about the recent volcanic eruption near Tonga.
SPACE-1-1.jpg (897×868) (leibovitvrnewsletters.com)
Investment implication: Concerns about the negative impact of global warming on the economy will be relieved temporarily. Energy prices over the next 2-3 years are likely to remain elevated.
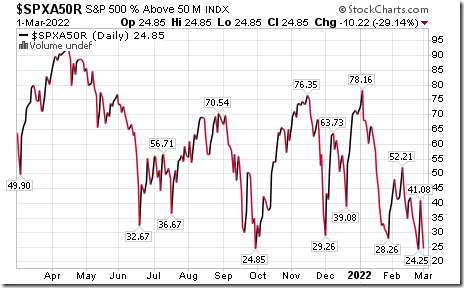
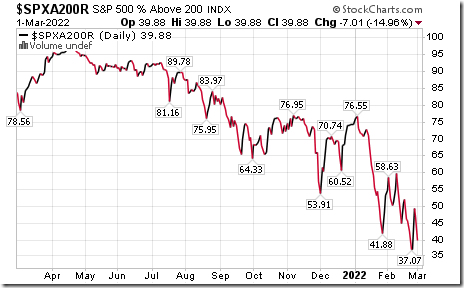
S&P 500 Momentum Barometers
The intermediate term Barometer plunged 10.22 to 24.85 yesterday. It remains Oversold, but has yet to show signs of bottoming.
The long term Barometer dropped 7.01 to 39.88 yesterday. It returned to Oversold on a drop below 40.00.
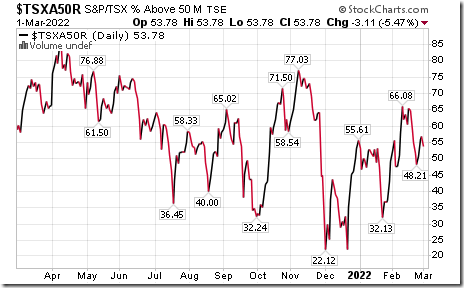
TSX Momentum Barometers
The intermediate term Barometer dropped 3.11 to 53.78 yesterday. It remains Neutral.
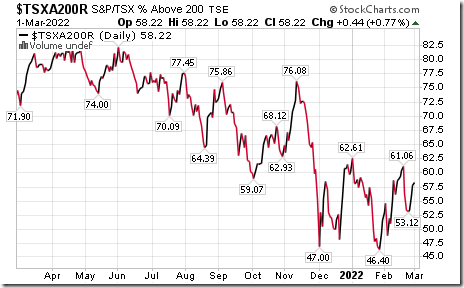
The long term Barometer added 0.44 to 58.22 yesterday. It remains Neutral.
Disclaimer: Seasonality and technical ratings offered in this report and at
www.equityclock.com are for information only. They should not be considered as advice to purchase or to sell mentioned securities. Data offered in this report is believed to be accurate, but is not guaranteed
This post was originally publised at Vialoux's Tech Talk.