Emerging Markets Radar (December 2, 2013)
Strengths
- Brokerage firms were positively surprised by the scope and tone of the recently proposed reforms by China’s government. While implementation is crucial and will take time, they believe that the prospect of reform will drive a re-rating of the Chinese equity market, narrowing the valuation gap versus the rest of the region. They recommend overweighting in Chinese H shares and A shares.
- China’s October profits at major industrial companies increased 15.1 percent year-over-year, down from 18.4 percent in September, according to the NBS. The deceleration is mainly due to a higher comparison base as industrial profit growth recovered in third-quarter 2012. In year-to-date terms, profits rose 13.7 percent in the first 10 months compared with 13.5 percent in the first nine months.
- China’s health care industry sales grew 19.9 percent year-over-year in October, up from 18.1 percent in September and 15.1 percent in October 2012. Industry profit was up 18.7 percent in October versus 17.8 in September 2013 and 14.3 percent in October 2012.
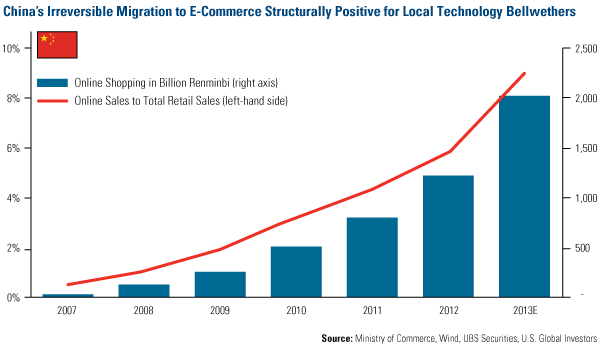
- China is the largest online market. According to I-Research, China’s internet population surpassed that of the U.S. in 2006 and the number of smartphone users surpassed those in the U.S. in first half of 2013. Online sales have increased 19 times over the past five years. Online penetration rate reached 6.3 percent in 2012, already surpassing 5.1 percent in the U.S. About 33 percent of apparel, footwear and sportswear sales in China were online in 2012 versus 5 percent in 2008.
- Yingluck Shinawatra, the prime minister of Thailand, survived a no confidence vote. On the economic front, Bank of Thailand, the central bank, cut interest rates by 25 basis points to help the weakening economy. Thailand’s current account turned a surplus from a deficit in September, and private consumption index was flat versus a negative change in September, indicating the economy is stabilizing, though not out of woods yet.
- Korea industrial production (IP) growth rose in October to 3.0 percent year-over-year and 1.8 percent month-over-month in October after dipping 3.9 percent in September, disrupted by one-off factors such as the automakers’ strike and Chuseok holidays.
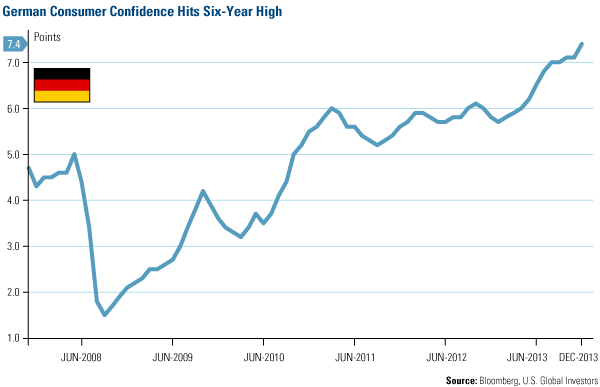
- European stocks climbed the most in almost two weeks as consumer confidence in Germany rose to a six-year high according to a GfK market survey. The research market group reported the mood among German households jumped to a higher-than-expected 7.4 points on the GfK scale, up from 7.1 points in the previous month. Analysts’ forecast for the period showed stagnation or a slight improvement at best. The GfK indicator is at its highest level since August 2007 coinciding with increases in German business climate and domestic demand as reported the prior week.
- Hungary’s central bank announced its 16th-consecutive benchmark rate reduction. The Monetary Council weighed the outlook for consumer prices, and remains supportive for further easing, even after policy makers lowered the benchmark rate by 20 basis points to 3.2 percent. The inflation rate fell to 0.9 percent in October, the lowest since 1974, and has remained below the central bank’s 3.0 percent target since February. The possibility of further reductions was made more likely when the European Central Bank (ECB) cut its benchmark rate on November 7 amid deflation risk.
Weaknesses
- Hong Kong’s October retail sales value was up 6.3 percent year-over-year versus consensus for 7.3 percent, the fourth-consecutive month to see single-digit growth. Luxury goods sales were 16.8 percent, while clothing and department store products were 10 percent.
- In October, Thailand’s trade deficit was widened to $1.8 billion after a $0.5 billion surplus in September, while exports showed 0.7 percent contraction year-over-year versus 7.1 percent contraction in September. Imports were down 5.4 percent in October versus down 5.2 percent in September. Thailand’s industrial production contracted 0.1 percent in October from September. Thailand’s auto sales were also down which forced the auto production utility rate to drop 12.4 points since November 2012 which may revert to the upside if auto exports pick up momentum.
- Foreigners were still net sellers throughout the week ($95.6 million) in the Philippines, and they have been net sellers in 17 of the 19 total trading days in November. Top names sold by foreigners this week were fundamentally healthy companies. The Philippines’ third-quarter GDP growth slowed to 7 percent from 7.6 percent in the second quarter.
- An HSBC report shows October’s monthly equity inflows are concentrated in developed market equity funds, with minimal flows to emerging market funds. Total equity inflows hit a nine-month high, but were mainly directed to developed market equity funds, reiterating this year’s trend. Despite a second consecutive week of inflows, appetite for emerging market equity funds remained low. Positioning data across the emerging market universe shows that, in spite of mild inflows, fund managers cut their exposure to overall emerging markets in their global portfolio to 7.3 percent, the lowest since August 2009.
- South Africa’s gross domestic product rose an annualized 0.7 percent in the three months through September, down from a revised 3.2 percent in the previous quarter. Africa’s largest economy is ailing after strikes demanding above-inflation wage increases in mining, construction and car manufacturing this year disrupted output, leaving economic growth on course to expand at the slowest pace since the 2009 recession.
Opportunities
- As shown in the chart above, the market share of online sales in China is rising quickly, accounting for nearly 9 percent of China’s retail sales now and still growing 50-60 percent per year. Taobao and Tmall’s online shopping platform recorded 35 billion renminbi in sales on November 11 2013, the so-called Single’s Day, representing 40 percent of national total retail sales on that day. Tencent’s Wechat attracts 500 million users to chat via mobile phone, capping the growth of voice calls and text messages to low-single-digits. The online platforms of Alibaba and Baidu take depositors less than 10 mouse clicks to buy a monetary fund product with a 4.5 percent annualized return.
- The European recovery has proved a tailwind to Dow Jones sales growth; at least one-third of the companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) reported revenue growth numbers from their European customers in the third quarter. During the previous quarter, only one-tenth of the companies in the industrials index reported revenue growth in Europe. This last quarter was also the highest number of DJIA companies to report sales growth in Europe since the fourth quarter of 2011, according to Scott Gooch of Jefferies. The results show the European recovery is gaining momentum which should benefit its main trading partners in Eastern Europe.
- China's premier, Li Keqiang, announced the reaching of an agreement with Hungary and Serbia to assist in building a railway between the two Eastern European countries. The project is set to jumpstart greater cooperation between China and Central and Eastern European countries. China, which now boasts the world's second-largest railway network and the longest mileage of high-speed rail tracks, can assist in the needs of Central and Eastern European countries for modern transportation and infrastructure.
Threats
- Indonesia fell short of its goal at the debut domestic dollar bond sale, indicating onshore liquidity is tight.
- Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff is expected to oppose Petrobras’ proposed fuel pricing formula, arguing it will impact gasoline prices and increase inflation. Petrobras currently sells fuel domestically at a sizeable discount to international market prices. The Presidential Palace also voiced concern over the proposed formula becoming a pricing reference for other regulated sectors, while it pondered if the process would take pricing and timing control from government hands. Backstage, presidential aides have commented the formula proposed by the board of Petrobras has been discarded. The effort now is to find a middle ground that allows for the company to increase prices closer to market prices, and increases the pricing predictability for financial planning purposes, while ensuring the executive retains some autonomy over the decision of future adjustments.
- The Russian ruble weakened to its lowest in more than four years on the back of corporate demand for foreign currency to meet debt payments. Russian companies are expected to pay back nearly $30 billion in principal of foreign debt in December, highlighting both the need for substantial amounts foreign currency, and the considerable leverage of Russian corporations. The ruble has been under pressure by consumer prices running at 6.3 percent, well above the central bank’s target.